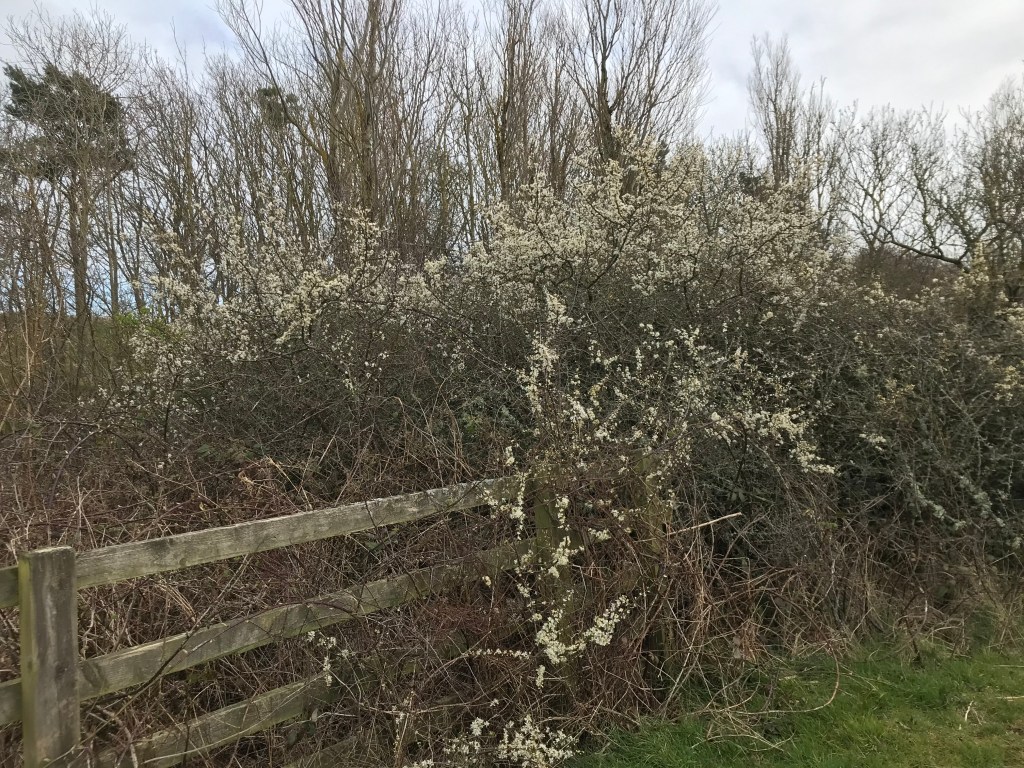
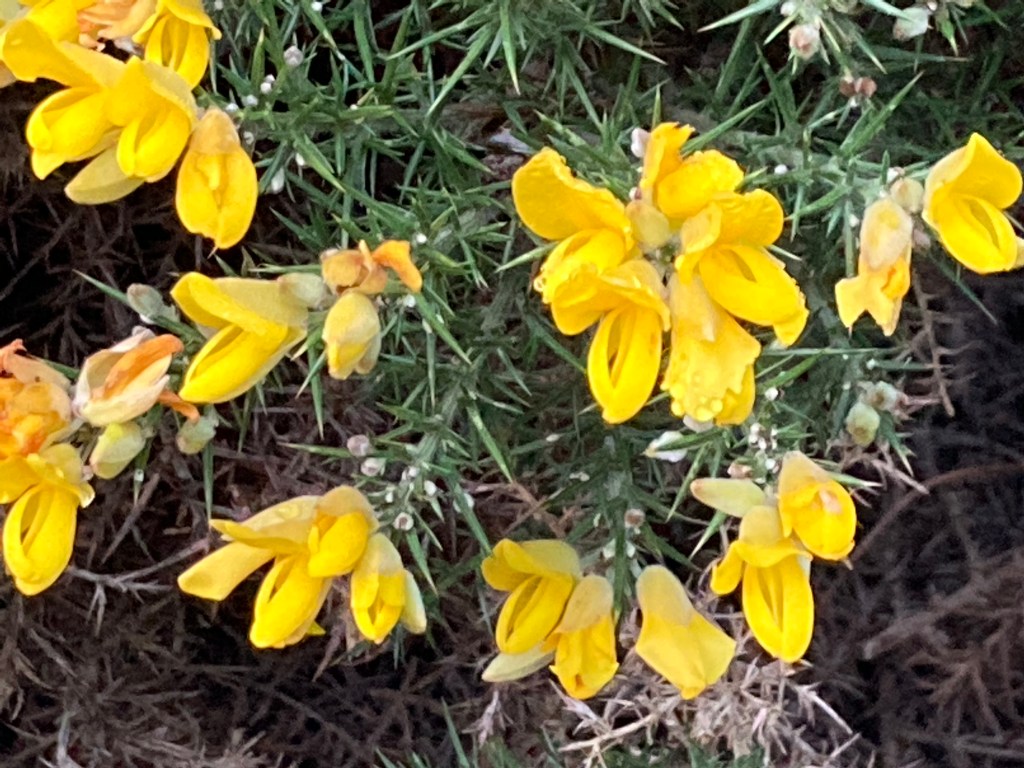
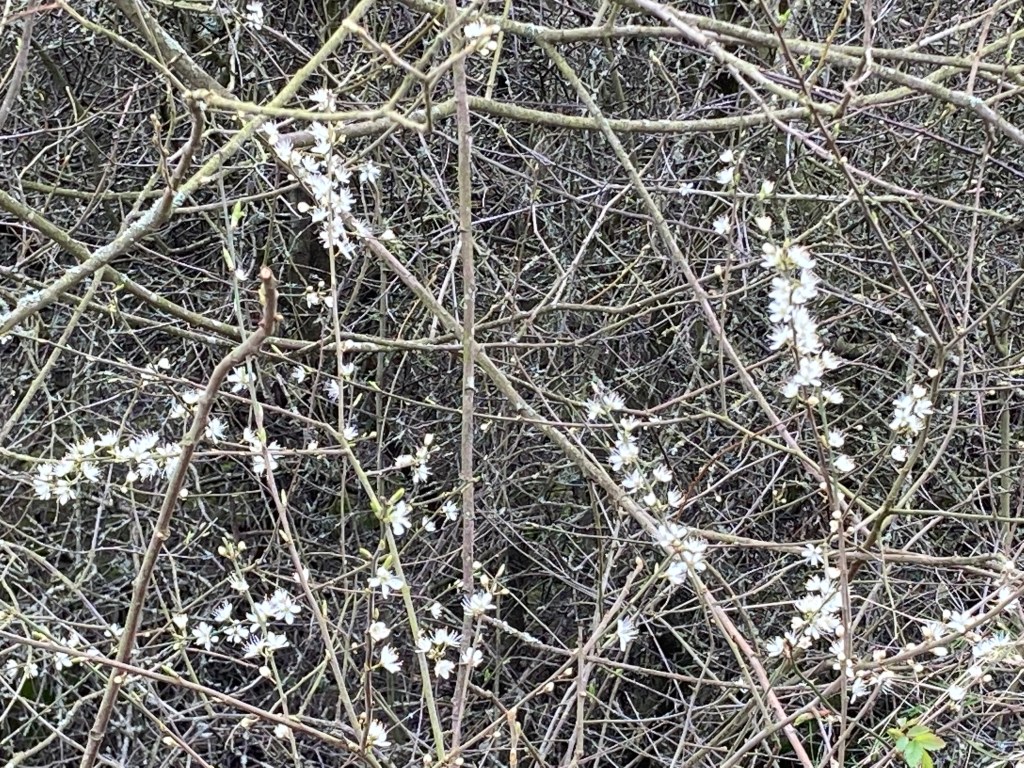
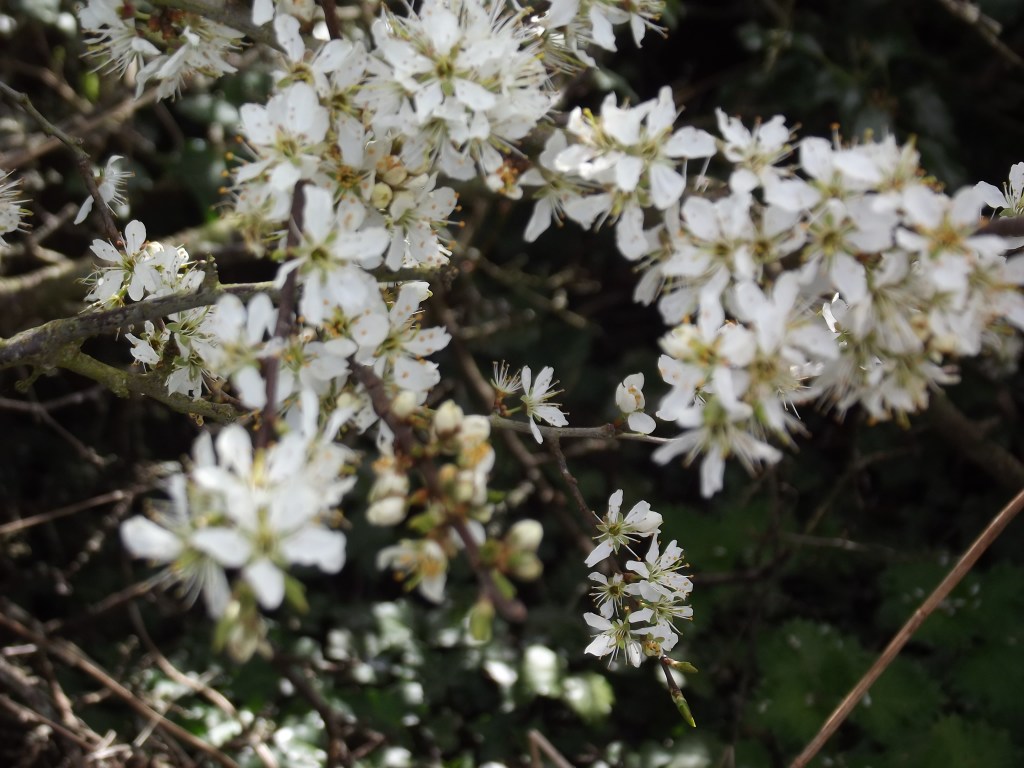
The frothy white blossom of the blackthorn has been in flower for the last month, standing out against the blackish twigs and branches, which have yet to come into leaf.

This shrub can grow to 4m or more and can be found in woodland or scrub, practically anywhere that the soil is not acid, but mainly grows in hedgerows, where the dense, thorny growth makes it an impenetrable barrier and protective nest sites for birds.
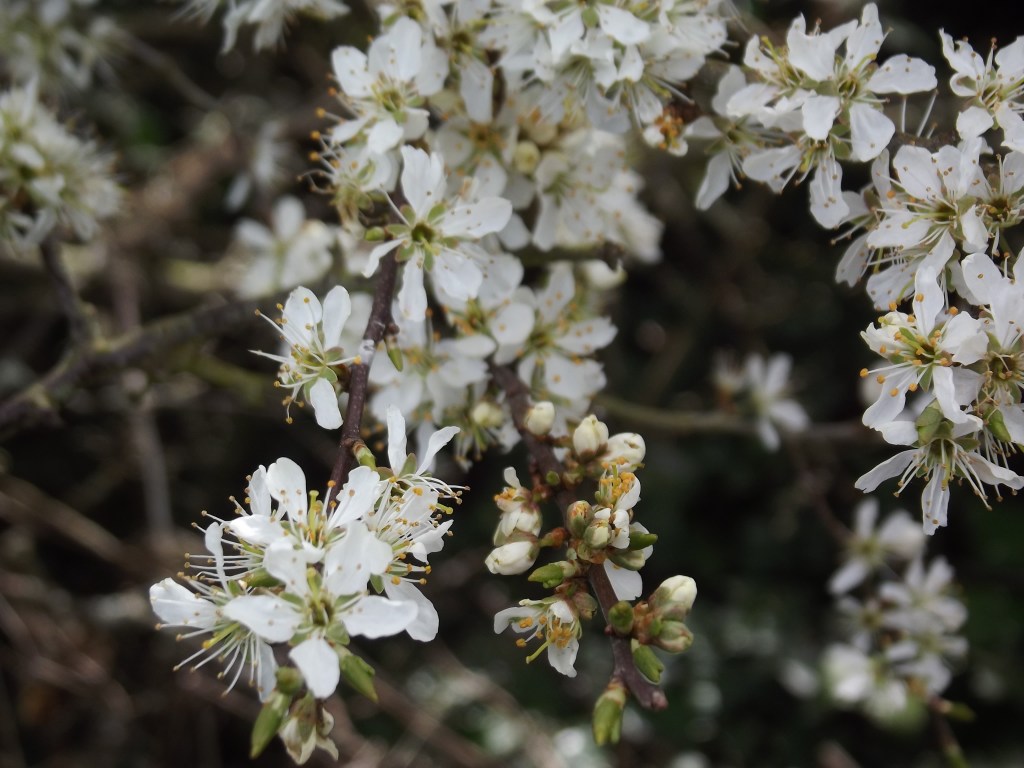

A member of the rose family and closely related to the plum and damson, the blackthorn is a native to Europe and Western Asia.
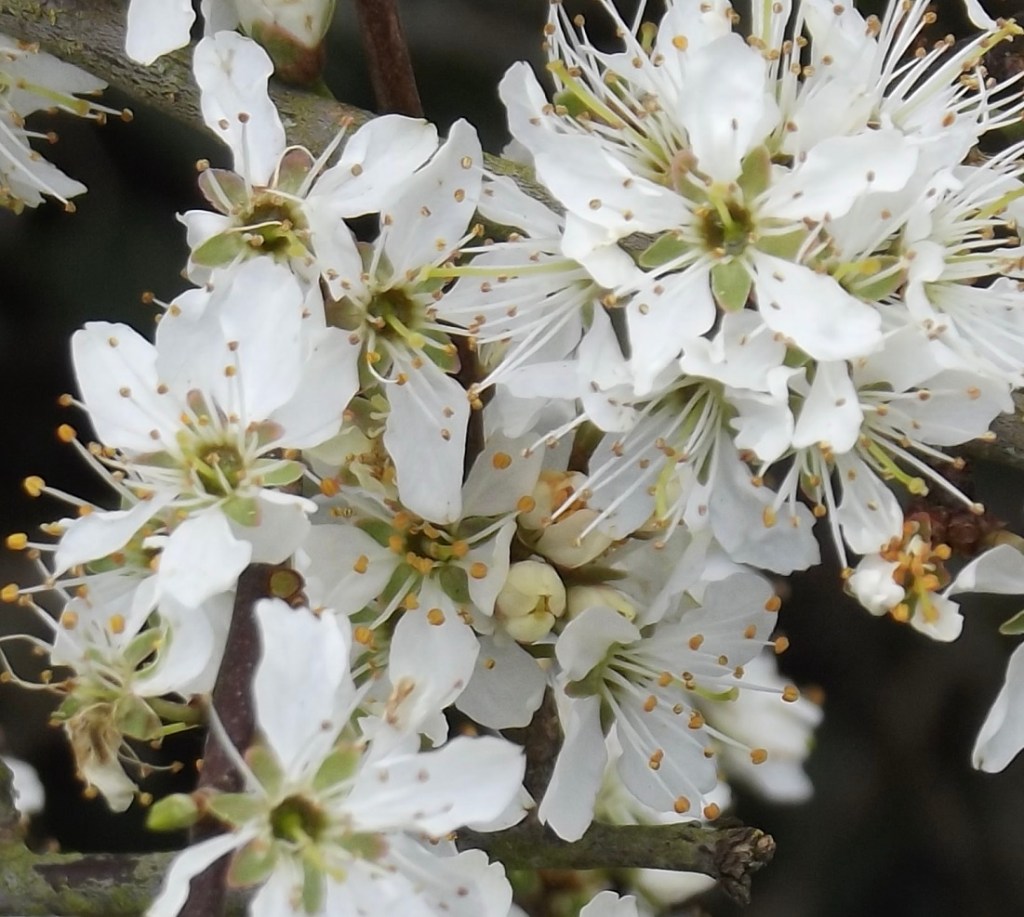
The flowers are hermaphrodite, each bearing both male and female parts and with five petals. They are the first flowers to appear in our hedgerows, arriving before the leaves and a welcome source of pollen and nectar for bees and other insects early in the year.

The small leaves are narrow and oblong shaped, tapering to a point and with toothed edges. They are the food plant for the caterpillars of several species of moths and butterflies, including the rare black hairstreak butterfly. In autumn they turn bright yellow.
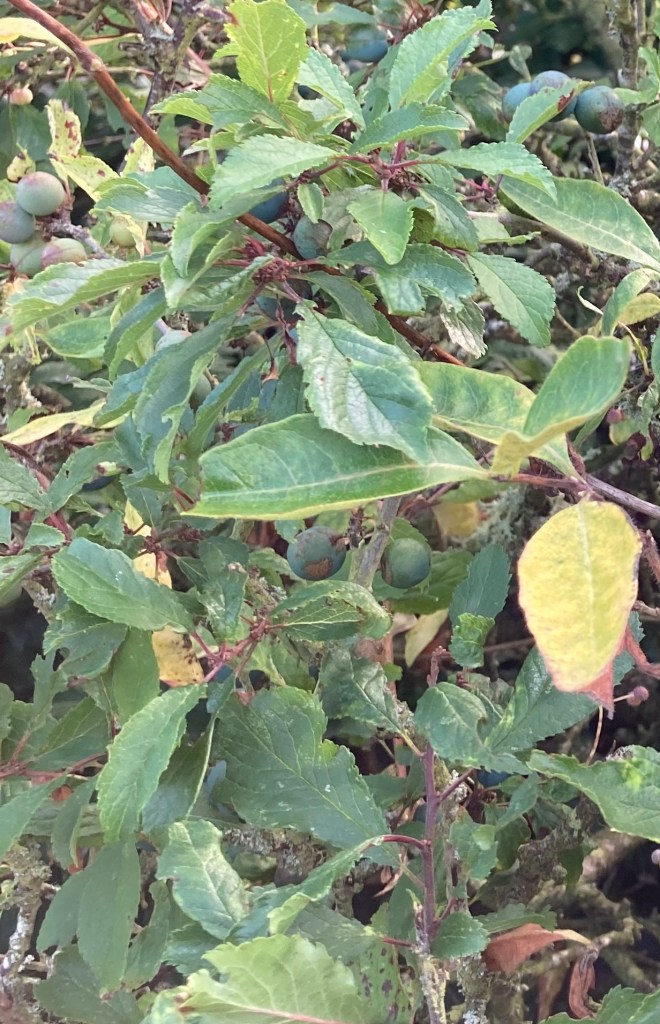

Also appearing in autumn are the sloes, round purple-black fruit with a bloom that gives them a blue tinge, each about 1cm in diameter. The sloe has a large stone and little flesh, but they do provide a valuable food source for birds, particularly for members of the thrush family.
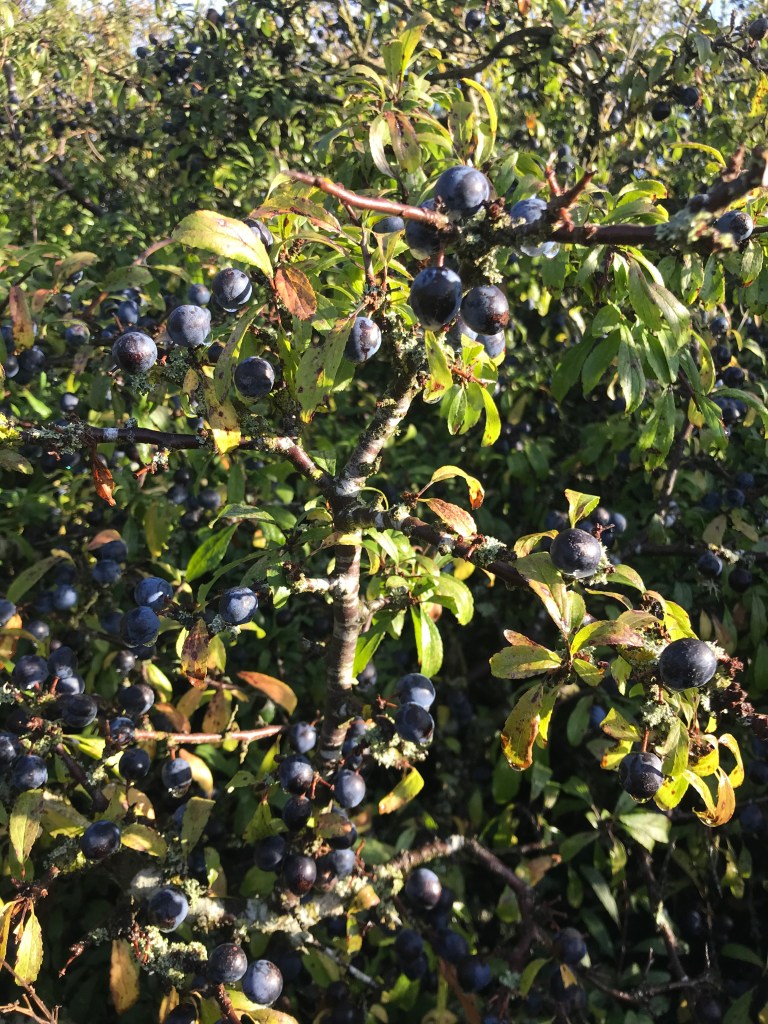

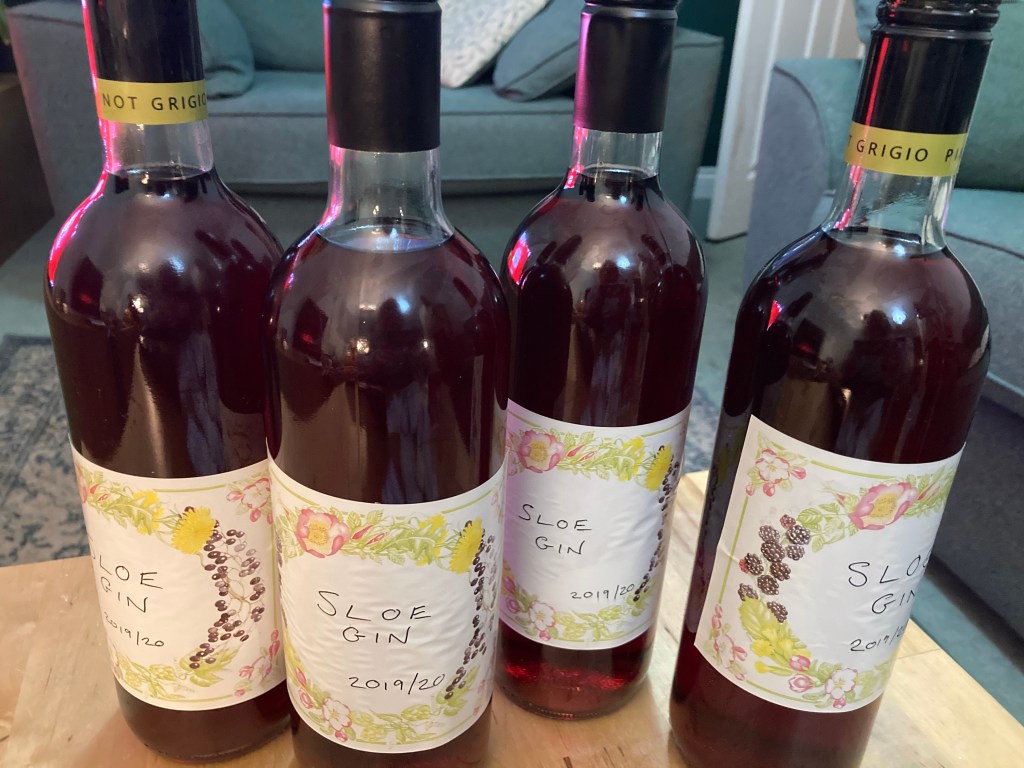
Sloes are incredibly sour, but sweeten slightly after the first frosts. In years where frosts damage the flowers and prevent the fruit from setting (or it is too cold for pollinating insects) the sloe crop is scarce. The fruit are used in sloe gin and can also be made into jams and jellies. You can read about how we make our own sloe gin here . If you have the patience to remove the stones from the fruit after they have been strained out of sloe gin (by which time they have absorbed a fair amount of alcohol, the flesh can be stirred into melted chocolate and left to set on a baking tray: delicious!

The wood of the blackthorn burns well and as it grows straight is used for walking sticks and tool handles. It was also said to be the wood of choice for witches’ staffs and wands and had an association with witchcraft.
Traditional medicine has used preparations of the plant used for cleansing the blood, for digestive disorders and rheumatism.
I always look out for the first blackthorn blossom to appear every spring, with the hope of a good crop to make sloe gin later in the year.

Don’t forget the following when picking any parts of a wild plant.
- Don’t touch or pick any plant unless you are ABSOLUTELY CERTAIN that it is safe to use, and not poisonous.
- Don’t pick anything unless it is abundant
- Only pick small amounts and no more than you need
- Don’t pick if there is a risk of pesticide/weedkiller or other contamination, including from traffic or other forms of pollution.
- Always get permission from the landowner.
- Avoid areas which may be soiled by animals (wild or farm animals or pets)
- Wash plants thoroughly